Surprisingly, soluble recombinant ICAM-1 expressed in one of the most widely used transient expression systems, human embryonic kidney cells and derivatives hereof has only been used for malaria binding assays in very few studies. Recombinant AbMole Clofentezine protein yield is generally higher in HEK than CHO cells, and can reach several hundred milligrams of recombinant protein per litre of culture medium. Thus the HEK expression system has the potential to produce large quantities of recombinant ICAM-1 as well as the ability to produce recombinant proteins with appropriate human posttranslational modifications. In this study, we compared ICAM-1 expression in HEK293, COS-7, and mouse myeloma NS0 cells, in terms of protein purity, yield, folding, the ability to bind a recombinant DC4containing PfEMP1 protein, and relative cost. Neural tube defects are a class of human birth defects that result from a failure of embryonic neural tube closure. Failure to complete low spinal closure causes spina bifida, incomplete cranial closure results in anencephaly, while the failure of closure of the entire neural tube is a defect referred to as craniorachischisis. Worldwide, NTDs affect 0.5-2 per 1,000 live born infants, with varying prevalence across populations. Spina bifida and anencephaly are the two most common forms of NTDs, occurring in 0.5-1 per 1,000 pregnancies in the United States. Many infants with spina bifida can survive, but may endure a greatly diminished quality of life. Although genetic factors are believed to contribute in part, to the etiology of spina bifida, the elucidation of such factors has remained elusive. This is likely due to the complex inheritance pattern and the contribution of a range of environmental factors including folic acid. Indeed, more than 250 genes were causally linked to NTDs in mice. Homozygous PCP mutations, such as Vangl2 D255E and S464N, Celsr1 D1040G and N1110K, produced a craniorachischisis phenotype in mice. When heterozygous PCP gene mutations such as Vangl2 D255E are combined with non-PCP mutations in mice, they produce embryos with spina bifida or exencephaly. In humans, mutations in PCP core genes including VANGL2, FZD6, CELSR1, PRICKLE and DISHEVELLED, are associated with several kind 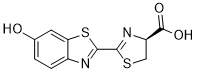 of NTDs. including spina bifida, anencephaly and craniorachischisis. SCRIB is a PCP-associated gene in mammals. It is a member of the LAP protein family. The LRR region and PDZ regions are important for SCRIB localization and stabilization at the plasma membrane. The SCRIB PDZ domain also plays an important role in physical interaction with other proteins, including the core PCP gene Vangl2, which has a PDZ binding domain. In Drosophila, homozygous Scrib mutations result in loss of apicobasal cell polarity and neoplastic tissue overgrowth. In mice, homozygous Scrib mutations, such as circletail and line-90, cause the most severe type of NTD, craniorachischisis.
of NTDs. including spina bifida, anencephaly and craniorachischisis. SCRIB is a PCP-associated gene in mammals. It is a member of the LAP protein family. The LRR region and PDZ regions are important for SCRIB localization and stabilization at the plasma membrane. The SCRIB PDZ domain also plays an important role in physical interaction with other proteins, including the core PCP gene Vangl2, which has a PDZ binding domain. In Drosophila, homozygous Scrib mutations result in loss of apicobasal cell polarity and neoplastic tissue overgrowth. In mice, homozygous Scrib mutations, such as circletail and line-90, cause the most severe type of NTD, craniorachischisis.